Cloud
In simple terms, cloud computing allows you to rent instead of buy your IT. Rather than investing heavily in databases, software, and hardware, companies opt to access their compute power via the internet, or the cloud, and pay for it as they use it. These cloud services now include, but are not limited to, servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and business intelligence.
Cloud computing provides the speed, scalability, and flexibility that enables businesses to develop, innovate, and support business IT solutions.
The cloud enables users to access the same files and applications from almost any device, because the computing and storage takes place on servers in a data center, instead of locally on the user device. This is why a user can log in to their Instagram account on a new phone after their old phone breaks and still find their old account in place, with all their photos, videos, and conversation history. It works the same way with cloud email providers like Gmail or Microsoft Office 365, and with cloud storage providers like Dropbox or Google Drive.
Businesses today turn to the cloud to drive agility, deliver differentiation, accelerate time-to-market, and increase scale. The cloud model has become the standard approach to build and deliver applications for the modern enterprise.
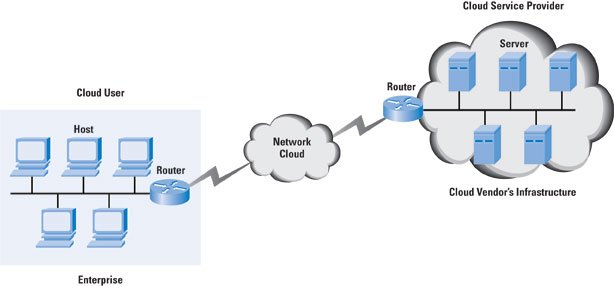
Cloud networking has also played a critical role in the way organizations address their growing infrastructure needs, regional expansions, and redundancy plans. Many organizations are adopting a multi-data center strategy and leveraging multiple clouds from multiple cloud service providers (CSPs).
Benefits of cloud networking
Most organizations have become a patchwork of on-premises technologies, public cloud services, legacy applications and systems, and emerging technologies — a complex situation that contributes to a weak security posture and results in inadequate governance, visibility, and manageability across fragmented networks.
A Virtual Cloud Network is VMware’s vision of the future of networking. It is an architectural approach (not a product) built in software at global scale from edge-to-edge, that’s able to deliver consistent, pervasive connectivity and security for apps and data wherever they reside, independent of underlying physical infrastructure. Whether your workloads are on premises or in the cloud, the same network and security stack can be used to provide connectivity, security, and visibility. It is also the kind of next-generation networking service consumption technology that IT is increasingly adopting to provide the digital fabric that helps unify a hyper-distributed world.